Understanding motion is the first step to mastering physics in Class 9. In this blog post, we bring you well-structured and easy-to-understand Motion Class 9 Notes based on the NCERT Science Chapter 7.
This chapter introduces the concept of motion and explores how objects move in our everyday life. It starts by discussing how motion is relative and depends on the observer’s point of view. It then explains different types of motion — straight-line (rectilinear), circular, uniform, and non-uniform motion — and introduces key physical quantities like distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration. The chapter also teaches how to represent motion graphically using distance-time and velocity-time graphs, and how to use equations of motion to calculate various parameters. It ends with the concept of uniform circular motion, highlighting how an object can accelerate without changing its speed, simply by changing direction.
🏁 What is Motion?
In everyday life, motion is all around us — cars moving, birds flying, rivers flowing.
In physics, motion is defined as a change in position of an object with time relative to a reference point.
🔁 Types of Motion
- Rectilinear (Straight Line) Motion
- Circular Motion
- Vibrational Motion
- Periodic and Non-periodic Motion
📏 Distance and Displacement
- Distance is the total path traveled (scalar).
- Displacement is the shortest path from the starting to the endpoint (vector).
📌 Key Point: Displacement can be zero even if distance is not.
⏱️ Speed and Velocity
- Speed = Distance / Time (scalar)
- Velocity = Displacement / Time (vector)
- Average Speed and Average Velocity are useful for non-uniform motion.
🔼 Acceleration
- Change in velocity per unit time.
- Formula: a=v−uta=tv−u
- Positive acceleration = speeding up
- Negative acceleration = slowing down
📊 Graphical Representation
- Distance-Time Graphs
- Straight line → Uniform speed
- Curve → Non-uniform speed
- Velocity-Time Graphs
- Area under graph = distance covered
📐 Equations of Motion
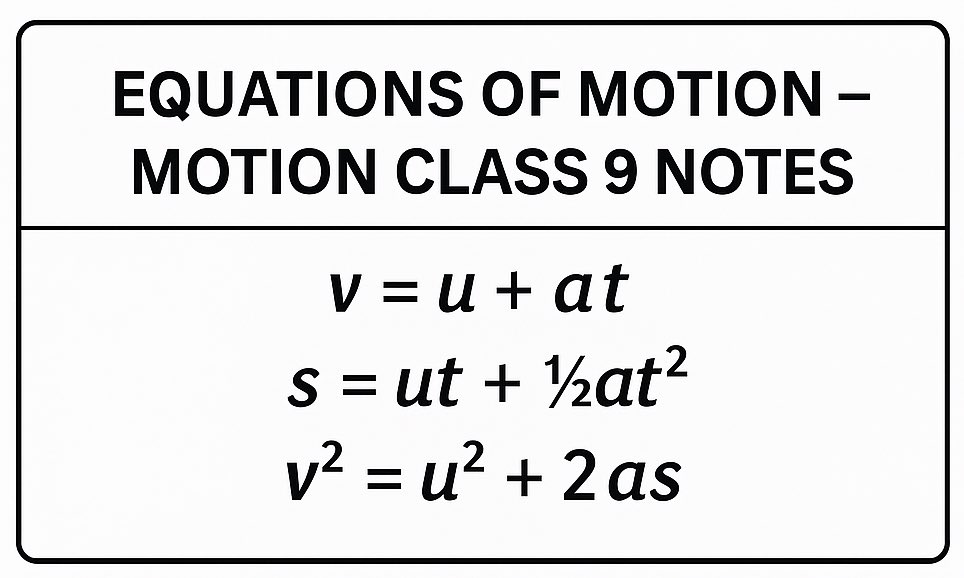
These help calculate final velocity, displacement, and time in uniformly accelerated motion.
🌀 Uniform Circular Motion
An object moving in a circle at constant speed is in uniform circular motion. Though speed is constant, direction changes, so the object is accelerating.
Whether you’re preparing for exams or just revising, these Motion Chapter Class 9 Notes and Class 9 Motion Notes cover all important concepts with examples, formulas, and graphs to help you learn smarter, not harder.
See more:
Motion Class 9 NCERT Solutions for Exercises!
For more Class 9 Science Chapters, click here!
