Human capital formation is the process of enhancing the skills, knowledge, and health of individuals to make them more productive and valuable to the economy.Human capital formation in India, has been a critical driver of economic growth and development. By investing in education, healthcare, and vocational training, India has transformed its vast population from a potential liability into a valuable asset. Initiatives like the Green Revolution and the IT boom highlight how human capital formation can revolutionize sectors and boost national productivity.
What is Human Capital Formation?
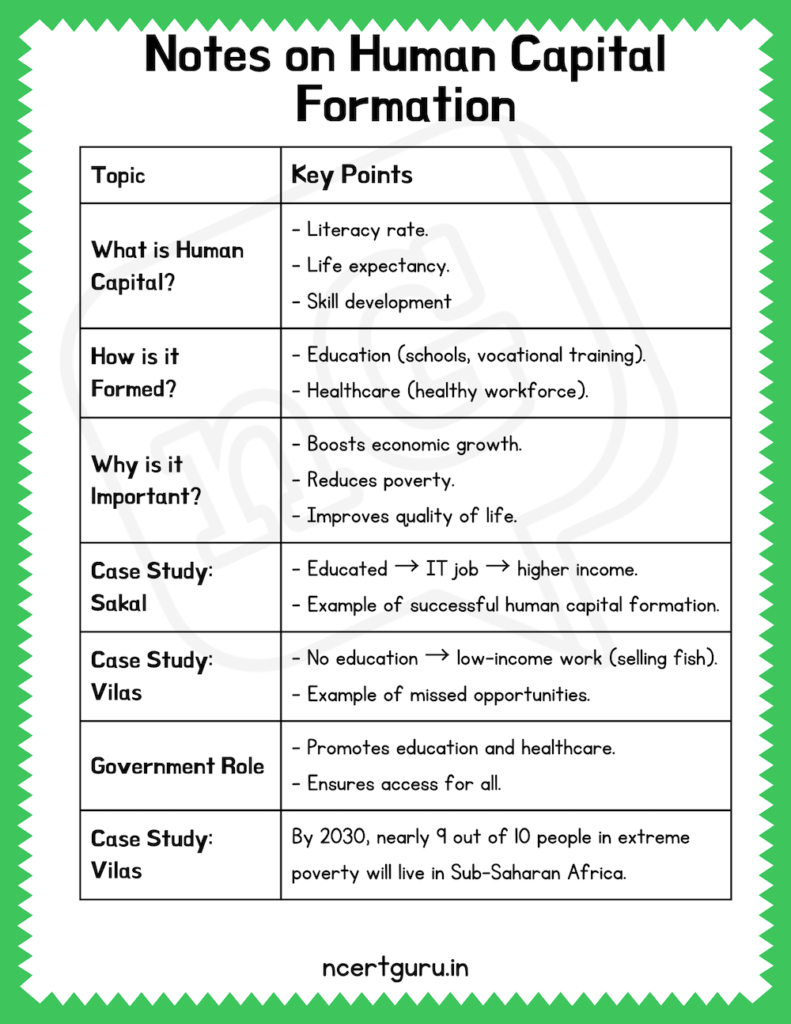
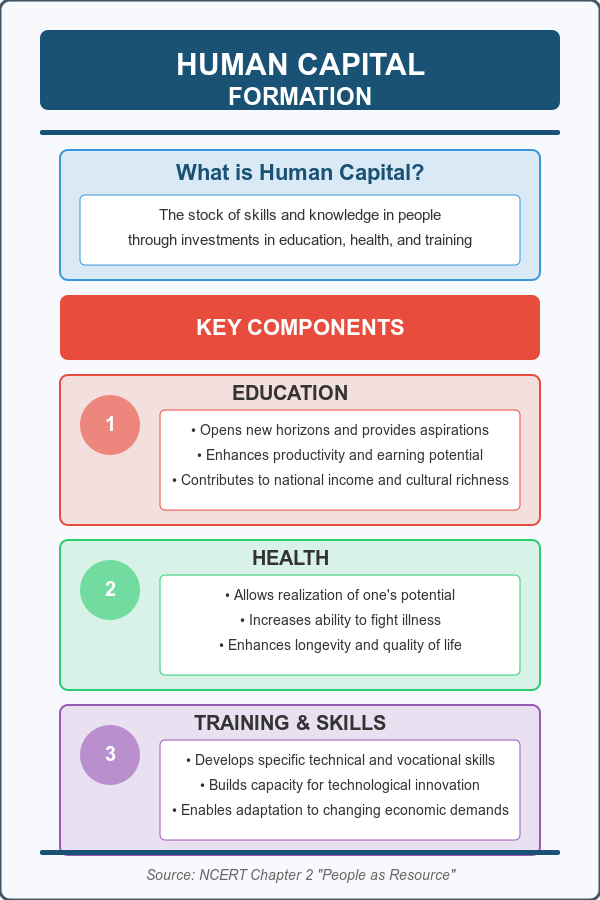
- Definition: The process of acquiring and increasing the number of skilled, educated, and healthy individuals who are productive and contribute to the economy.
- Key Idea: Human capital is created through investments in education, training, and healthcare.
Importance of Human Capital Formation
- Economic Growth: Educated and healthy individuals are more productive, leading to higher incomes and GDP growth.
- Example: Sakal’s education → job in IT → higher income.
- Societal Benefits: A healthier and more educated population benefits society as a whole.
- Example: Green Revolution (knowledge + technology → increased agricultural productivity).
- Global Examples:
- Japan: Despite lacking natural resources, Japan invested heavily in human capital (education, health) and became a developed nation.
How is Human Capital Formed?
- Education:
- Formal education (schools, colleges).
- Vocational training (e.g., Sakal’s computer course).
- Healthcare:
- Healthy individuals are more productive and can work efficiently.
- Example: A healthy worker is less likely to miss work due to illness.
- On-the-Job Training:
- Learning new skills while working (e.g., Sakal designing software at his job).
Returns on Investment in Human Capital
- Direct Returns:
- Higher income for individuals (e.g., Sakal’s salary after education).
- Indirect Returns:
- Societal benefits (e.g., educated parents invest more in their children’s education).
- Long-Term Impact:
- Creates a virtuous cycle of development (educated → healthier → more productive → higher income).
Case Study: Sakal vs. Vilas
- Sakal:
- Invested in education and training → got a job in IT → higher income.
- Example of human capital formation.
- Vilas:
- No investment in education or healthcare → stuck in low-income work (selling fish).
- Example of missed opportunities for human capital formation.
Government’s Role in Human Capital Formation
- Education Initiatives:
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan: Universal elementary education.
- Mid-Day Meal Scheme: Encourages school attendance and improves nutrition.
- Navodaya Vidyalayas: Quality schools in rural areas.
- Healthcare Initiatives:
- National Health Policy: Focus on accessible healthcare.
- Ayushman Bharat: Health insurance for low-income families.
Key Concepts Related to Human Capital Formation
- Literacy Rate: Percentage of people who can read and write.
- Higher literacy → better human capital.
- Life Expectancy: Average number of years a person is expected to live.
- Higher life expectancy → healthier workforce.
- Skill Development: Vocational training and on-the-job learning.
- Example: Sakal’s computer course → job in IT.
Source: NCERT Economics Class 9, Chapter 2 – People as Resource
📚 Explore More Topics!
Dive deeper into NCERT Economics Class 9 People as a resource with our comprehensive summaries and notes. Go back to pick up another topic and ace your exams!
Test Your Knowledge!
Ready to challenge yourself? Take our Human Capital Formation MCQ Online Test and see how well you’ve mastered the concepts. Click here to start the quiz now!
📇 Learn Smarter, Not Harder!
Revise key terms and concepts with our Human Capital Formation Flashcards. Perfect for quick revision and last-minute prep.

Pingback: Types of Unemployment in India Notes: NCERT Economics Class 9 - NCERT guru
Pingback: Human Capital Formation MCQ: Online Test - NCERT guru
Pingback: People as Resource: Overview - NCERT guru